Corporate Human Rights Benchmark: Pilot Methodology 2016
The CHRB pilot methodology assessed the top 100 companies across the agricultural products, apparel and extractives industries on their human rights policies, processes and performance.
The 2018 Corporate Human Rights Benchmark assesses 101 of the largest publicly traded companies in the world on a set of human rights indicators. The companies from 3 industries – Agricultural Products, Apparel, and Extractives – were chosen for the first Benchmark on the basis of their size (market capitalisation) and revenues and assessed across 6 Measurement Themes which have different weightings. Even though average scores are low across the board, overall companies tend to perform more strongly on policy commitments and management systems than on remedy or dealing with key risks in practice.
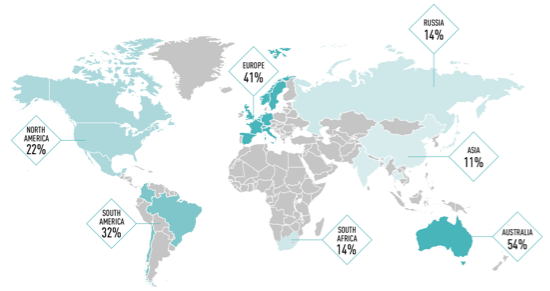
Average scores per region (source: CHRB 2018)
Some key takeaways from the results

The CHRB pilot methodology assessed the top 100 companies across the agricultural products, apparel and extractives industries on their human rights policies, processes and performance.
This Benchmark focuses on 98 companies of the three industries: Agricultural Products, Apparel, and Extractive. It is grounded in the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights, as well as additional standards and guidance focused on specific industries and...
The Human Trafficking Initiative works to address the issue of child sex trafficking in Greater Atlanta. Sexual exploitation is the most damaging form of child abuse.
We are pleased to share a new report that captures the movements of migrant workers coming to Malaysia, based on data contributions from International Domestic Workers Federation, Persatuan Sahabat Wanita Selangor, Migrant CARE Malaysia, Human Traff...Read More
By Stéphane Brabant and Elsa Savourey Companies are currently establishing their first vigilance plans and preparing to effectively implement them. However, clarifications are still needed with regard to the interpretation and practical application...Read More
Research conducted by Labour Rights Promotion Network (LPN) and Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School (JHSPH) of Public Health Center for Refugee and Disaster Response, and supported by the United Nations Inter-Agency Project on Human Trafficking (UNIAP). ...Read More