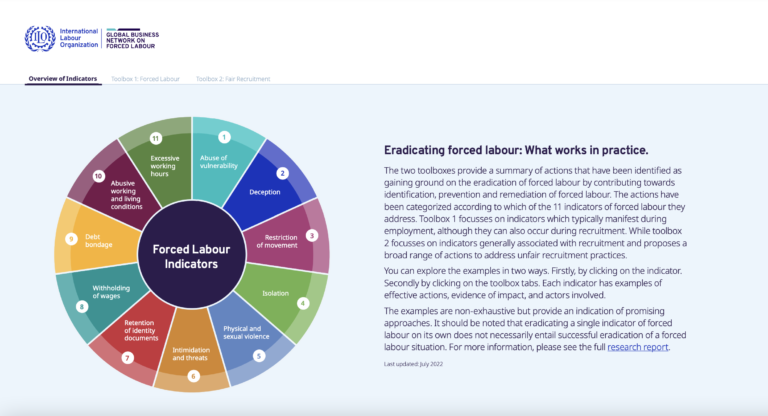
How can forced labour be eradicated globally? What approaches are the most effective at gaining ground towards this goal, and can they be replicated across country contexts? There are many ideas about what could work in theory, but there still is little data, despite decades of recognizing forced labour as a global problem, on what has actually worked in practice. Much of the knowledge about what works is held by a range of stakeholders addressing these issues on the ground.
This study finds that the global eradication of forced labour requires a whole-of-society approach. A wide range of actors have a role to play, including Governments, enterprises, labour recruiters, employer and business membership organizations, worker organizations, migrant community-based organizations, international organizations, including the International Labour Organization (ILO) and United Nations agencies, civil society organizations, technical experts, multi-stakeholder platforms and initiatives, faithbased organizations and media outlets. While collaboration across these stakeholder groups is critical, this study focuses on key approaches at the Government level and the company level as a first step.